Publications, projects, and other resources appear below.
NEW SCHOOLS IN THE UNITED STATES: A QUANTITATIVE REVIEW OF NEW PUBLIC SCHOOLS OPENED OVER THE LAST THREE DECADES
Jesse Margolis
May 2023
This study, commissioned by the Carnegie Corporation of New York, provides a comprehensive review of new public schools opened in the United States between 1990-91 and 2019-20. We find that nearly 17 million children (one third of all public school students in the country) attend a new school opened over the last three decades. As part of our study, we profile New York City – a district at the forefront of the new schools movement – and provide tools and data for other researchers to extend our analysis. Read the full report.
ECONOMIC AND RACIAL INTEGRATION THROUGH SCHOOL CHOICE IN NEW YORK CITY
Jesse Margolis, Daniel Dench, and Shirin Hashim
July 2022
A version of our evaluation of integration efforts in New York City has been published in the peer-reviewed journal Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis. In this study, we find that New York City’s District 15 – which set ambitious prioritization targets for economically disadvantaged students and eliminated academic screens – saw a decline in sixth-grade economic segregation by 55% and racial segregation by 38%. New York City’s District 3 – which set less ambitious targets and maintained screens – saw no significant change in segregation. The most up-to-date data on enrollment and segregation in all of New York State’s 700+ districts can be found on IntegrateNY.org.
THE IMPACT OF MIDDLE SCHOOL INTEGRATION EFFORTS ON SEGREGATION IN TWO NEW YORK CITY DISTRICTS
Jesse Margolis, Daniel Dench, and Shirin Hashim
July 2020
By some measures, New York State has the most segregated schools in the country. To address segregation, many school districts in the state have begun to develop integration plans. Two of farthest along are New York City’s Community School District 3 in Manhattan and Community School District 15 in Brooklyn, which are among the most diverse and segregated school districts in the state. In advance of the 2019-20 school year, both District 3 and District 15 implemented a ‘controlled choice’ admissions process for rising sixth graders that prioritized economically disadvantaged students. While the broad contours of the two plans were similar, they differed in several important details, and the results varied dramatically. In this study, we evaluate the impact of both integration efforts on segregation and seek to explain their divergent results. Read the full report.
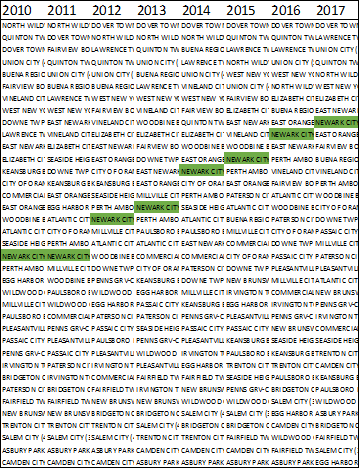
RESILIENCE: WILL URBAN SCHOOLS THAT BEAT THE ODDS CONTINUE TO DO SO DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC?
Jesse Margolis and Eli Groves
June 2020
In the United States, schools that serve high concentrations of poor, Black, and Latino students tend to do worse on measures of achievement than schools that serve a wealthier, whiter population. However, there are exceptions. In this study, we analyze 50 of the largest cities in the US and estimate the share of students in each city who attend a ‘beat-the-odds’ school, defined as a school with test scores substantially higher than would be predicted by student and school characteristics. We also dive more deeply into the data in Newark, New Jersey, the city with the highest beat-the-odds rate, to better understand its results. In a companion brief, we explore how these same cities are adapting to remote learning and meeting new challenges in the age of COVID-19. Read the full report.
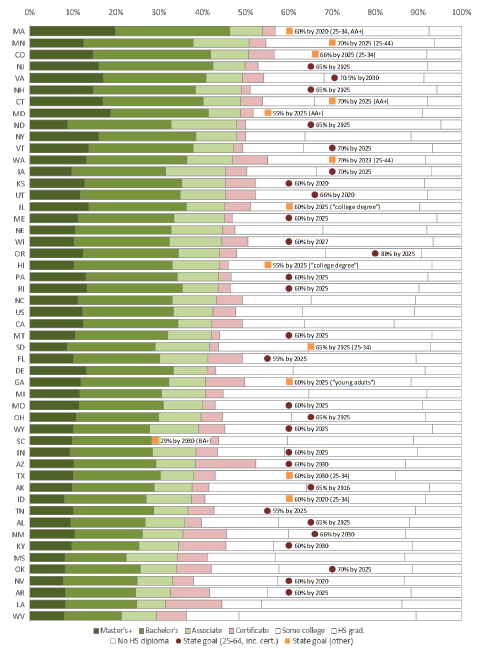
RAISING THE BAR: WHAT STATES NEED TO DO TO HIT THEIR AMBITIOUS HIGHER EDUCATION ATTAINMENT GOALS
James Dean Ward, Jesse Margolis, Benjamin Weintraut, and Elizabeth Davidson Pisacreta
February 2020
A higher education degree is increasingly important in today’s economy. Yet, the fewer than half of U.S. residents between the age of 25 and 64 have a higher education credential. Given this imbalance, over the past decade, nearly all states have developed and publicized specific goals for postsecondary attainment. In this report, we partner with ITHAKA S+R to assess how states are doing against those goals. To do this, we developed a projection tool that forecasts long-run changes in state-by-state attainment levels based on a combination of past trends and user-generated assumptions about the future. In addition to releasing our report, we are also making the tool publicly available, in the hopes that states will find it useful as they set or revise their higher education attainment goals. Read the full report.
A NEW BASELINE: PROGRESS IN NEWARK’S DISTRICT AND CHARTER SCHOOLS FROM 2006 TO 2018
Jesse Margolis and Eli Groves
June 2019
Over the past two decades, since its school district was taken over by the state, Newark, NJ has undertaken numerous large-scale reforms in public education, including charter school expansion, closure or replacement of underperforming schools, curriculum redesign, negotiation of a new teachers contract, and the development of a universal application system. In February 2018, based on improved results and a collaborative agreement between Newark’s mayor and the state-appointed superintendent, New Jersey returned control of Newark’s district schools to the city. Therefore, the 2017-18 school year serves as a reasonable end-point to the period of state-control. This report tracks Newark student performance through this end-point, and in doing so, provides a new baseline against which to measure Newark’s future progress under local control. Read the full report.
SETTING A NORTH STAR: MOTIVATIONS, IMPLICATIONS, AND APPROACHES TO STATE POSTSECONDARY ATTAINMENT GOALS
Cindy Le, Elizabeth Davidson Pisacreta, James Dean Ward, and Jesse Margolis
June 2019
Higher education attainment goals can serve as a ‘north star’ to guide states’ postsecondary policies, investments, and agendas. The extent to which state attainment goals lead to substantive improvements in college-going rates, college graduation rates, postsecondary credential attainment rates, and reductions in labor market skills gaps is as yet unclear. Further, the likelihood a state will meet its attainment goals varies by state and depends on contextual factors that are within and outside the purview of the education sector. In this issue brief written with researchers from ITHAKA S+R, we discuss the motivations, implications, and approaches states are taking to set and achieve their postsecondary attainment goals. Read the issue brief.
THREE-YEAR MAP GROWTH AT SCHOOLS USING TEACH TO ONE: MATH
Jesse Margolis
February 2019
Teach to One: Math (TtO) is an innovative model of teaching mathematics that re-envisions the way in which teachers, students, and curriculum interact in middle and high school classrooms to provide a more personalized learning experience for every student. Through a technology-infused mix of direct instruction, collaborative work with peers, and individualized learning, TtO seeks to introduce students to mathematics content at the right level for them. This study compares three-year math test score growth on the NWEA’s MAP test at all 14 schools that used TtO from 2015-16 to 2017-18 to a national reference group, controlling for each student’s starting score. This study also begins to explore the relationship between the content students are presented with during the year and their subsequent test score gains. See more and read the full report.
NEWARK ENROLLS: A PRINCIPLED APPROACH TO PUBLIC SCHOOL CHOICE
Kimberly Austin, Lucero Batista, Mahua Bisht, Andrew Karas, Jesse Margolis, and Andy Sonnesyn
April 2018
Newark Public Schools (NPS), in partnership with most of the city’s charter schools, developed a universal enrollment system in 2013. Like a growing number of cities, Newark adopted universal enrollment to lessen the impact of resource and other inequalities on families’ ability to exercise school choice. Newark’s system, called Newark Enrolls, was to be guided by seven principles: choice, access, community, equity, reliability, ease, and transparency. With four enrollment cycles completed and over 36,000 students placed, the Newark community is now in a position to assess the impact of Newark Enrolls. In this report, MarGrady Research and the Center for Public Research and Leadership (CPRL) at Columbia University use quantitative and qualitative data to examine enrollment patterns and practices under Newark Enrolls. See more and read the full report.
MOVING UP: PROGRESS IN NEWARK’S SCHOOLS FROM 2010 TO 2017
Jesse Margolis
October 2017
Newark’s public schools entered the national spotlight in 2010 when it was announced that $200 million in private philanthropy would be donated to the school district. This gift supported numerous significant reforms in the city’s public schools, and these reforms generated substantial upheaval, as has been well documented elsewhere. Less well documented is the progress the city’s public schools have made over the past seven years. The study seeks to fill that gap, taking multiple approaches to analyzing progress in Newark using student test scores at the elementary and middle school level, the graduation rate at the high school level, and student enrollment at all levels. Where possible, this study also replicates earlier work by other researchers, updating their analysis with the most recent data available. See more and read the full report.